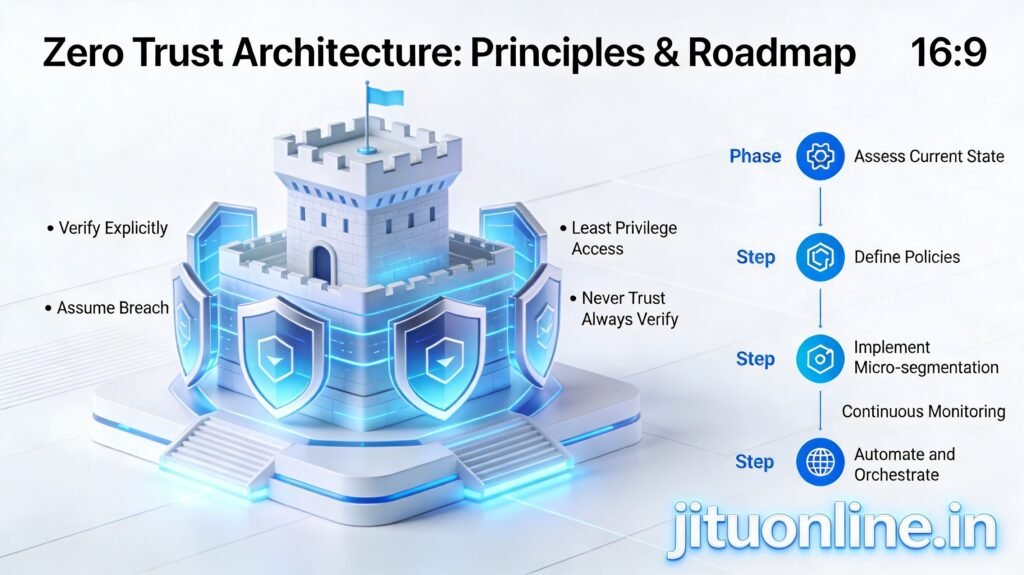
Zero Trust Architecture (ZTA) eliminates implicit trust, verifying every user, device, and request regardless of location. It assumes breach and enforces continuous validation, microsegmentation, and least-privilege access.
Core Principles of Zero Trust
- Identity-Centric Security: Verify users and devices, not network location.
- Least-Privilege Access: Grant minimal permissions needed for tasks.
- Microsegmentation: Isolate network zones to limit lateral movement.
- Continuous Monitoring: Validate every access request in real-time.
- Dynamic Policy Enforcement: Adjust controls based on risk levels.
Essential Components
- Policy Engine: Evaluates access requests.
- Policy Administrator: Enforces decisions.
- Policy Enforcement Points: Security checkpoints for traffic.
- Key pillars: Identity, Devices, Networks, Applications/Workloads, Data (CISA model).
Phased Implementation Roadmap
Deploy ZTA in stages for manageable rollout. Adapt timelines to organizational needs.
Phase 1: Foundation Building
- Deploy global DNS filtering (e.g., Cisco Umbrella, Cloudflare Gateway).
- Monitor/filter inbound emails for phishing.
- Identify SaaS misconfigurations (CASB tools).
- Assess assets, data flows, and current tools; secure executive buy-in.
Phase 2: Identity and Authentication
- Establish identity provider (e.g., Azure AD, Okta); enforce MFA everywhere.
- Enforce HTTPS/DNSSEC; TLS decryption for threats.
- Zero Trust for public apps; close inbound ports.
- Clean identities, device health checks, anomaly detection.
Phase 3: Segmentation and Protection
- Inventory apps; enforce ZTNA for SaaS/private apps.
- Segment networks; MDM for devices; data discovery.
- Microsegment networks; encrypt data; secure APIs/cloud.
- Inventory devices/APIs; endpoint protection (e.g., CrowdStrike).
Phase 4: Operational Integration
- Hardware MFA (Yubico); SOC for monitoring.
- Broadband WAN; activity logging; DLP for sensitive data.
- DevOps automation; auto-scaling.
- Automate policies; analytics; regular testing.
Example Implementation Timeline Table
| Timeline | Goal | Relevant Products |
|---|---|---|
| Phase 1 | Deploy global DNS filtering; email filtering; SaaS discovery | Cisco Umbrella, Cloudflare Gateway, Zscaler |
| Phase 2 | Corporate identity + MFA; HTTPS enforcement; ZT for apps | Azure AD, Okta, Cloudflare Access, ZPA |
| Phase 3 | App inventory; network segmentation; MDM; data discovery | Cloudflare Zero Trust, Intune, Yubico |
| Phase 4 | Hardware MFA; SOC; endpoint protection; DLP; automation | Yubico, CrowdStrike, Splunk, Terraform |
Business Value and Challenges
- Reduce incidents by 33%; halve breach costs; speed compliance 30-50%.
- Address integration: Map systems first to cut time by 40%.
Governance and Culture
- Define policy owners, risk thresholds, reviews.
- Train staff; appoint champions; communicate changes.
Reference frameworks: NIST SP 1800-35, NSA/DoD guidelines, CISA Maturity Model, Microsoft Zero Trust.
Latest posts by Jitendra Chaudhary (see all)
- N8N Python Docker Setup: Self-Hosting Struggles vs. Competitors - February 11, 2026
- Zero Trust Architecture Principles and Implementation Roadmap - February 9, 2026
- Build AI Web Apps with Gemini AI Studio No Code - February 9, 2026
Connect With Me Facebook page Instagram Linkedin Twitter/X: Twitter/X Email : jitu9968 at gmail dot com